US Dollar in the green while markets fear a possible hawkish Fed

- The US Dollar trades in the green against most of its major peers, with a big surge against the Turkish Lira.
- Traders assess the impact of the upcoming Federal Reserve rate decision.
- The US Dollar Index is still stuck between 103.00 and 104.00 for now.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar (USD) against six major currencies, ticks up and recovers to 103.60 at the time of writing on Wednesday. The surge in the Greenback comes on the back of a steep pop of over 5% in the USD against the Turkish Lira (TRY) after headlines emerged that authorities detained Istanbul mayor Ekrem Imamoglu, President Tayyip Erdogan’s main political rival, on charges including corruption and aiding a terrorist group.
On the economic data front, it is a very calm day in the runup towards the Federal Reserve (Fed) decision on interest rates later in the day. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is set to announce its policy rate decision and publish the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) update. After the meeting, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell will comment in a press conference. With the Trump policy in the backdrop, markets will want to know how many, if any, rate cuts the Fed members have penciled in for 2025 and beyond.
Daily digest market movers: Tensions between expectations and Fed
- At 18:00 GMT, the Fed will release its Interest Rate Decision and Monetary Policy Statement, along with the Summary of Economic Projections.
- The policy rate is expected to remain unchanged in the 4.25%-4.50% range.
- Besides that, the Interest Rate Projections in the SEP update might suggest how many rate cuts the Fed expects for 2025 and 2026.
- At 18:30 GMT, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell will deliver a statement and take questions in a press conference.
- Equities show signs of some risk-on sentiment, with European indices and US futures trading in the green, though less than 0.50% on average.
- According to the CME Fedwatch Tool, the probability of interest rates being lower than current levels in May currently stands at 16.8%, compared to 21.5% on Tuesday. For June, the odds for borrowing costs being lower stand at 62.6%.
- The US 10-year yield trades around 4.29% and is very stable on the day, off its near five-month low of 4.10% printed on March 4.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: The posture more important than the pause
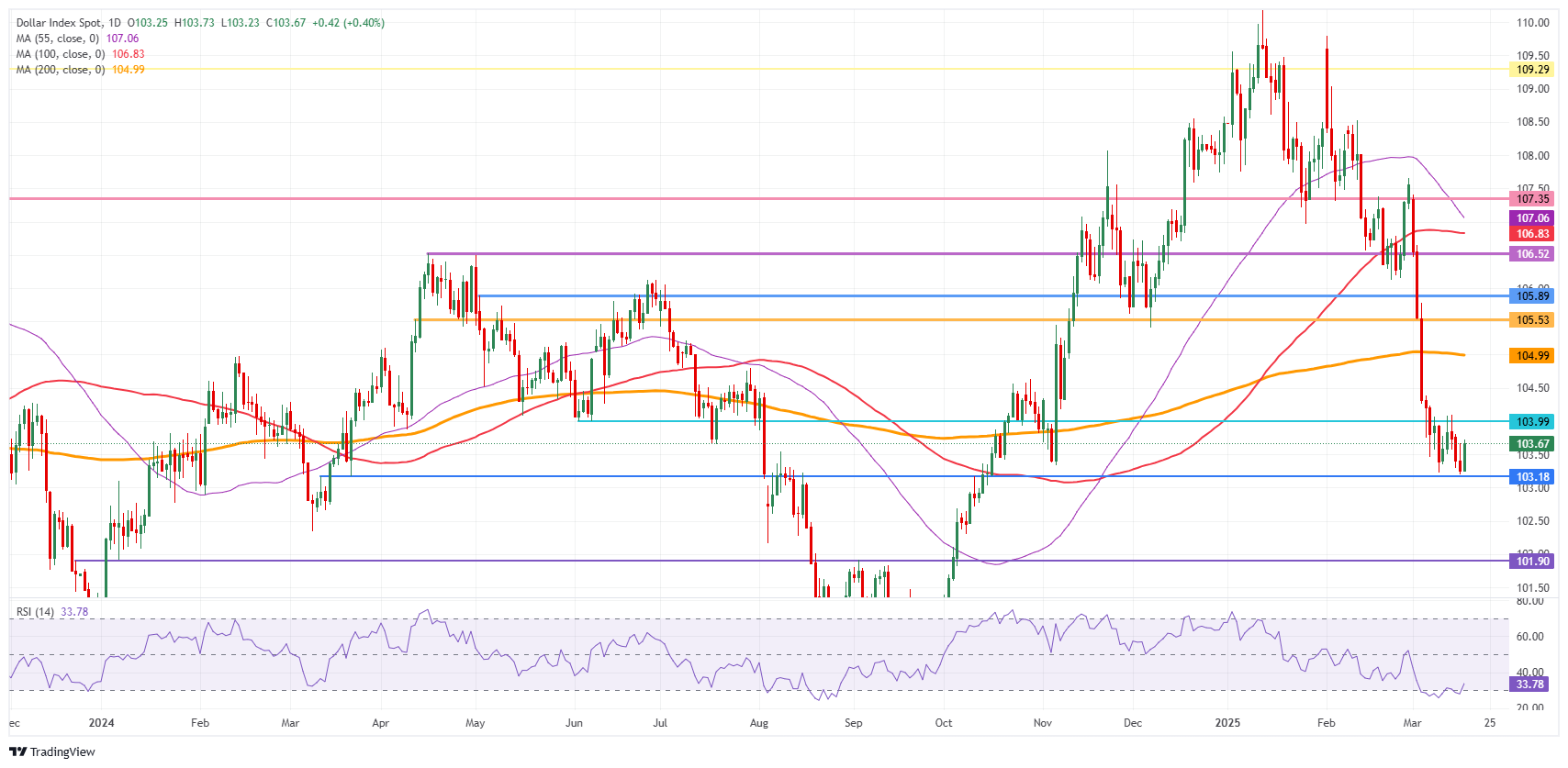
The US Dollar Index (DXY) withstood another firm pressure on its downside support level near 103.18 on Tuesday. The fact that the support can refrain the DXY from hitting a new six-month low suggests that markets are awaiting more clarity on tariffs, the US economy, inflation and geopolitics. The DXY is at a crossroads where, once the 103.18 level gets broken, might not come back for a long time now that several banks are starting to call for more US Dollar devaluation in the coming years, according to Bloomberg.
A return to 104.00 would mean the DXY simply stays loyal to its range for March. If bulls can avoid a technical rejection there, look for a large sprint higher towards the 105.00 round level, with the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) converging at that point and reinforcing this area as a strong resistance. Once broken through that zone, a string of pivotal levels, such as 105.53 and 105.89, will present as caps.
On the downside, the 103.00 round level could be considered a bearish target in case US yields roll off on the back of the Fed communication later this Wednesday, with even 101.90 not unthinkable if markets further capitulate on their long-term US Dollar holdings.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Source link